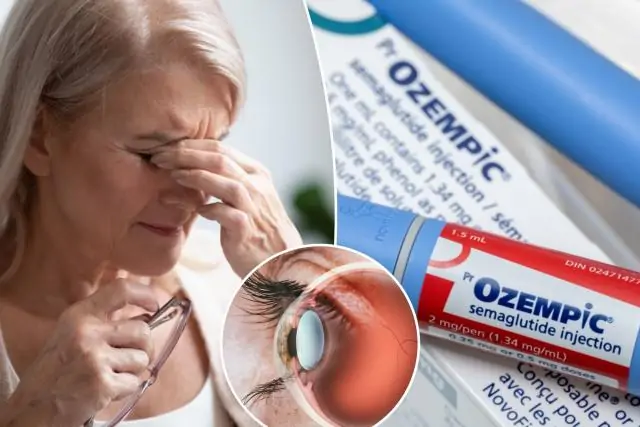
A study conducted at the Mass Eye and Ear Clinic has found a link between widely prescribed weight-loss medications and a rare but serious eye condition. Published in JAMA Ophthalmology, the study suggests that patients taking semaglutide-based medications, such as Ozempic and Wegovy, are at increased risk of developing a form of blindness caused by a disease of the optic nerve.
A study led by Dr. Joseph Rizzo, director of the neuro-ophthalmology service at Mass Eye and Ear, focused on non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION), a condition that can lead to sudden and irreversible vision loss. Although NAION is relatively rare in the general population, the study findings indicate a significantly increased risk for those prescribed semaglutide.
Researchers analyzed records of more than 16,827 patients treated at Mass Eye and Ear since Ozempic's launch in 2017. The results were striking:
- Patients with diabetes who were prescribed semaglutide were more than four times more likely to be diagnosed with NAION;
- In overweight or obese patients taking the drug, the risk of NAION increased more than sevenfold.
The researchers acknowledge several limitations of their study. Mass Eye and Ear Clinic has an unusually high incidence of rare eye diseases, and the study population was predominantly white. Furthermore, the total number of NAION cases observed over the six-year period was relatively small.
While the study does not prove a cause-and-effect relationship , it raises important questions about the potential side effects of these increasingly popular medications. As semaglutide's use continues to grow for both diabetes and weight loss, this study highlights the need for continued vigilance and further study of its long-term impact on eye health. Patients currently taking Ozempic, Wegovy, or other semaglutide-based medications should not panic and should discuss these findings with their physicians. The benefits of these medications in treating diabetes and obesity remain significant, but awareness of the potential risks is crucial for making informed decisions and managing patient care.