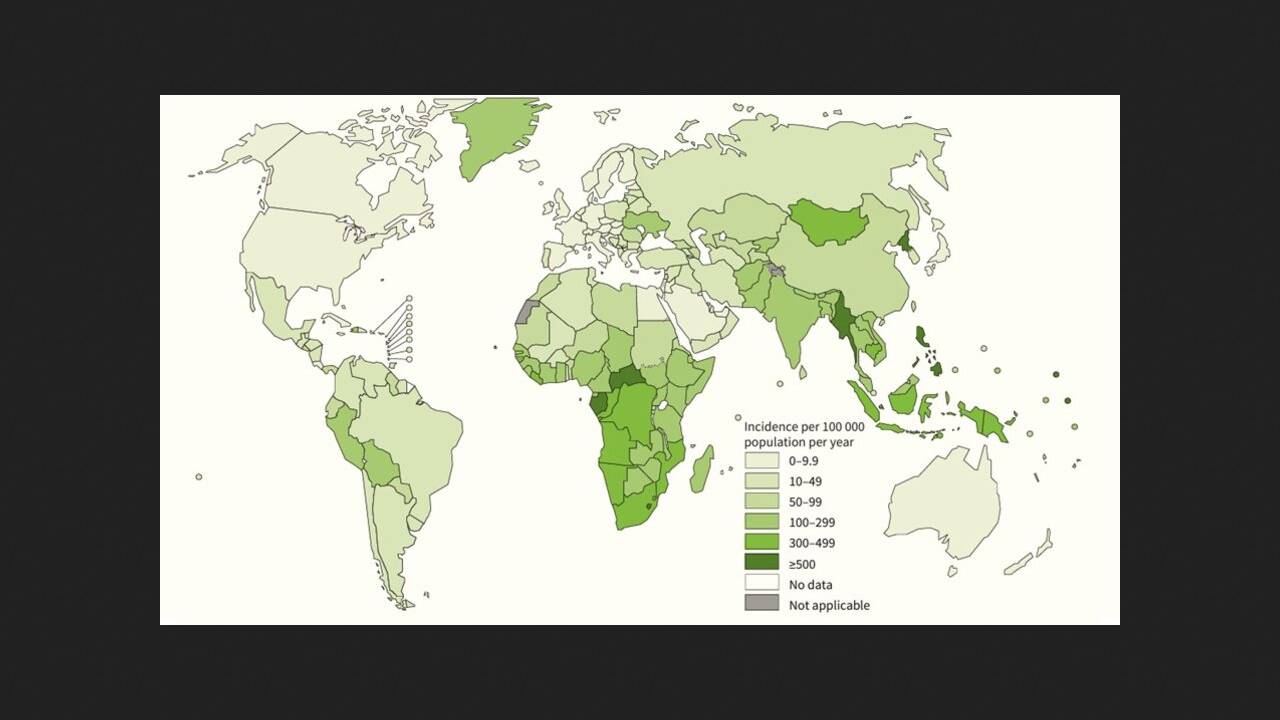
The World Health Organization has released its annual global tuberculosis situation report. According to it, there were 10.8 million people with tuberculosis worldwide in 2023 (10.7 million in 2022, 10.4 million in 2021), with 6.1 percent of cases occurring in people living with HIV. Experts attribute this increase to the impact of disruptions in tuberculosis services during the height of the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 and 2021. The incidence rate increased from 129 in 2020 to 134 cases per 100,000 population in 2023. However, the rate of incidence growth slowed significantly, to 0.2 percent between 2022 and 2023. The report was published on the WHO website.
In 2023, 8.2 million people worldwide were diagnosed with tuberculosis for the first time, the highest number ever recorded by WHO. In 2023, most people with tuberculosis lived in Southeast Asia, Africa, and the Western Pacific. Eight countries accounted for two-thirds of all tuberculosis cases: India, Indonesia, China, the Philippines, Pakistan, Nigeria, Bangladesh, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The highest number of people with multidrug-resistant tuberculosis in 2023 was identified in Russia and several countries in Eastern Europe and Central Asia. Meanwhile, the number of tuberculosis deaths decreased globally, from 1.32 million in 2022 to 1.25 million in 2023. However, disruptions to tuberculosis services due to the COVID-19 pandemic have led to an additional 700,000 tuberculosis deaths over four years.