Chinese and American researchers reported a successful trial treating a patient with severe systemic sclerosis using a commercially available preparation of NK lymphocytes with a chimeric antigen receptor, derived from donor induced pluripotent stem cells. The report was published in Cell.
Chimeric antigen receptor technology (read more about it in the article "Chimera vs. Cancer") was originally developed to modify T cells for tumor treatment. Its greatest success has been achieved in B-cell malignancies, as B cells possess highly specific antigens, CD19 and BCMA, which represent a good target for CAR T therapy. A similar approach has also been successfully used in clinical trials to treat various autoimmune diseases (the editors of Science, like Nature, named these experiments one of the key scientific achievements of 2024), as B cells play a key role in their pathogenesis. All these treatment regimens require isolating autologous T cells from the patient's blood, introducing the CAR transgene on a viral vector in the laboratory, expanding them, and reintroducing them into the body. Moreover, most patients develop typical complications after CAR T-lymphocyte infusion: cytokine release syndrome, neurotoxic syndrome ICANS, or hyperinflammatory syndrome IEC-HS of varying severity.
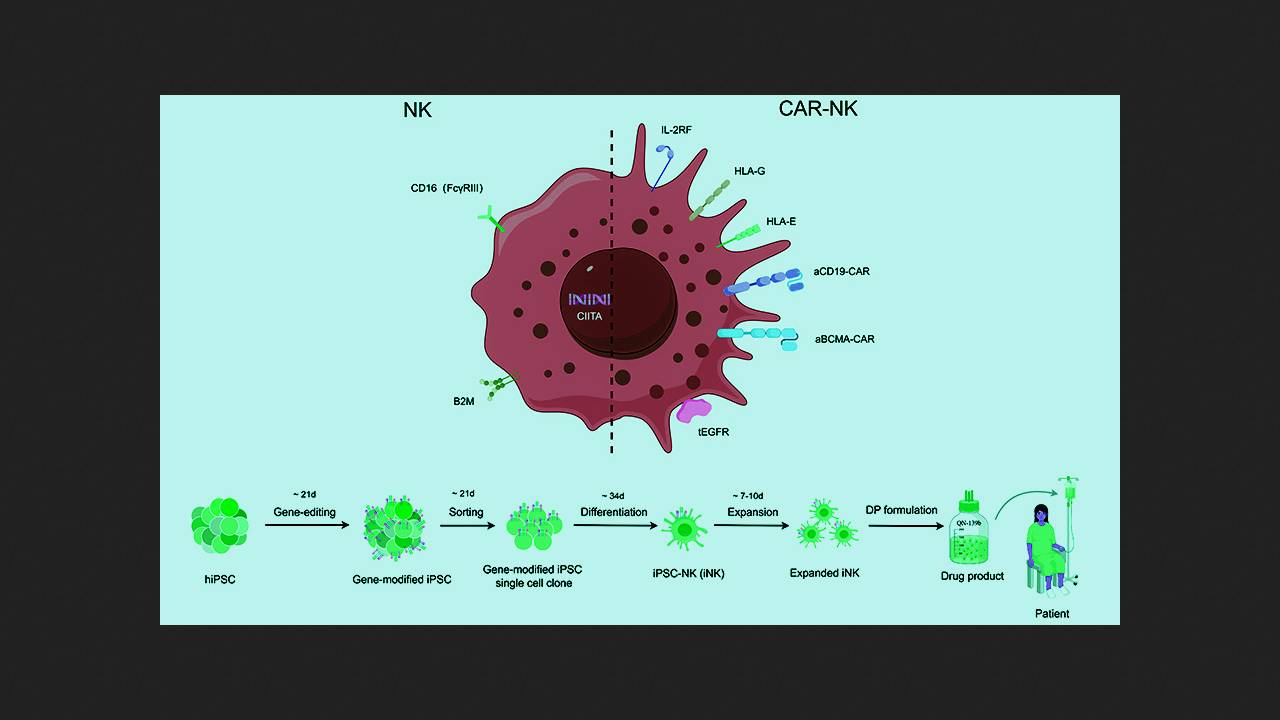
In preclinical and pilot clinical trials, the use of chimeric antigen receptor NK cells (CAR-NK cells) demonstrated significantly lower toxicity and potentially higher efficacy compared to CAR-T cells in the treatment of B-cell disease. Huji Xu of the Naval Medical University and Tsinghua University, along with colleagues and collaborators from Qihangene Biotech, decided to test CAR-NK cells in a severe, treatment-resistant autoimmune disease, using NK cells derived from donor induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) for their production. This approach is intended to simplify, reduce the cost, and standardize the procedure, as well as provide patients with a ready-to-use drug with no waiting time.
При создании экспериментального препарата QN-139b исследователи генетически донорские ИПСК с помощью редактора цитозиновых оснований для нокаута генов и системы CRISPR/Cas9 для сайт-специфичной интеграции желаемых модификаций. Успешно модифицированные клетки клонировали в культуре и дифференцировали в NK-лимфоциты. Внесенные модификации включали нокаут компонент главного комплекса гистосовместимости B2M и CIITA для предотвращения распознавания Т-клетками реципиента, а также нокаут мембранного иммуноглобулина CD16 и нокин человеческих лимфоцитарных антигенов (HLA) G и E для минимизации активации NK-клетками пациента. Кроме того, в клетки внесли конструкты, экспрессирующие рецепторы интерлейкина-2 (IL-2RF) для усиления активации и персистирования и рецептор эпидермального фактора роста (tEGFR) в качестве «аварийного выключателя» анти-EGFR антителами. Полученные клетки снабдили двумя типами CAR, нацеленными на CD19 и BCMA, отобрали успешно модифицированные, оценили их проточной цитометрией и анализом на функциональные маркеры и испытали на клеточных культурах и мышах.
Для участия в клиническом эксперименте авторы работы пригласили 36-летнюю женщину с тяжелой диффузной кожной системной склеродермией. В 16 лет у нее выявили синдром Рейно и высокий уровень (+++) специфичных для заболевания анти-Scl-70 антител. К 18 годам появились утолщения кожи конечностей, прогрессирующая эритема и боль в суставах, со временем кожные проявления распространились на лицо, шею и грудную клетку. За три года до поступления у женщины выявили интерстициальное поражение легких, непосредственно перед ним — умеренный фиброз миокарда с сохранной фракцией выброса. Многолетняя терапия метилпреднизолоном, циклофосфамидом, гидроксихлорохином, метотрексатом, микофенолата мофетилом, тоцилизумабом и нидабусиба этансульфонатом прогрессирование заболевания не остановила.
После лимфодеплеции пациентке провели четыре внутривенных инфузии 600 миллионов клеток QN-139b с интервалом в три дня. Пиковая концентрация CAR-NK-клеток (270 на миллилитр крови) и их доля в общем числе лимфоцитов (2,74 процента) наблюдались на седьмой день от первой инфузии и вернулись почти на исходный уровень к двенадцатому. Сразу после инфузии произошло резкое снижение уровня периферических В-лимфоцитов, который начал восстанавливаться через два месяца и продолжал через полгода, причем с преобладанием наивных В-клеток (что свидетельствует о перезагрузке иммунной системы). Также на фоне лимфодеплеции резко снизились уровни Т- и NK-лимфоцитов, которые начали восстанавливаться через две недели и продолжали через полгода. В течение шести месяцев наблюдались прогрессирующее снижение уровней аутоантител анти-Scl-70 и анти-SSA/Ro52, нормализация уровней компонент системы комплемента C3 и C4, стабильный уровень иммуноглобулина G, существенное снижение уровней иммуноглобулинов А и М и нормализация уровня иммуноглобулина Е (до лечения в разы повышенного).
Clinical findings included a reduction in disease manifestations according to the EUSTAR-AI scale from 3.68 to 1.33 points by the sixth month; improvements in three or more of the five CRISS scale points were at least 20 percent by the first month, 30 percent by the second, and 50 percent by the third. Regression of cutaneous fibrosis, edema, and erythema were observed visually, ultrasonographically, elastographically, and histologically; pulmonary fibrosis also significantly decreased, and myocardial fibrosis was virtually resolved. Capillaroscopy showed significant improvement in the microcirculatory bed, with evidence of new vessel growth. Quantitative blood proteomic analysis revealed increased expression of proteins associated with angiogenesis, suppression of connective tissue proliferation, oxidative stress response, and immunosuppression, and decreased expression associated with immune activation, inflammation, and fibrosis. No significant adverse reactions to therapy were identified, the level of the inflammatory marker C-reactive protein fluctuated within normal limits, and body temperature did not increase.
The results of a pilot clinical experiment show that CAR-NK lymphocytes from donor stem cells can be considered as a promising method for treating severe autoimmune diseases that are resistant to accepted treatment regimens.
In early 2025, American researchers reported the success of the first clinical trials of a ready-made drug of CAR-NK lymphocytes from donor iPSCs (FT596), which involved 86 patients with refractory or relapsed B-cell lymphoma.