Daiju Ueda and colleagues at Osaka Metropolitan University developed a model based on deep learning algorithms that effectively detects fatty liver disease (steatosis) in chest X-rays. The study used data from 4,414 patients at two Japanese clinics, who each underwent 6,599 chest X-rays and liver elastograms with controlled attenuation parameter (CAP, a quantitative measure of steatosis). Patients from one clinic were randomly assigned in an 8:1:1 ratio to datasets for training, tuning, and internal testing of the model, while participants from the second clinic were included in the external testing dataset. The results were published in the journal Radiology: Cardiothoracic Imaging.
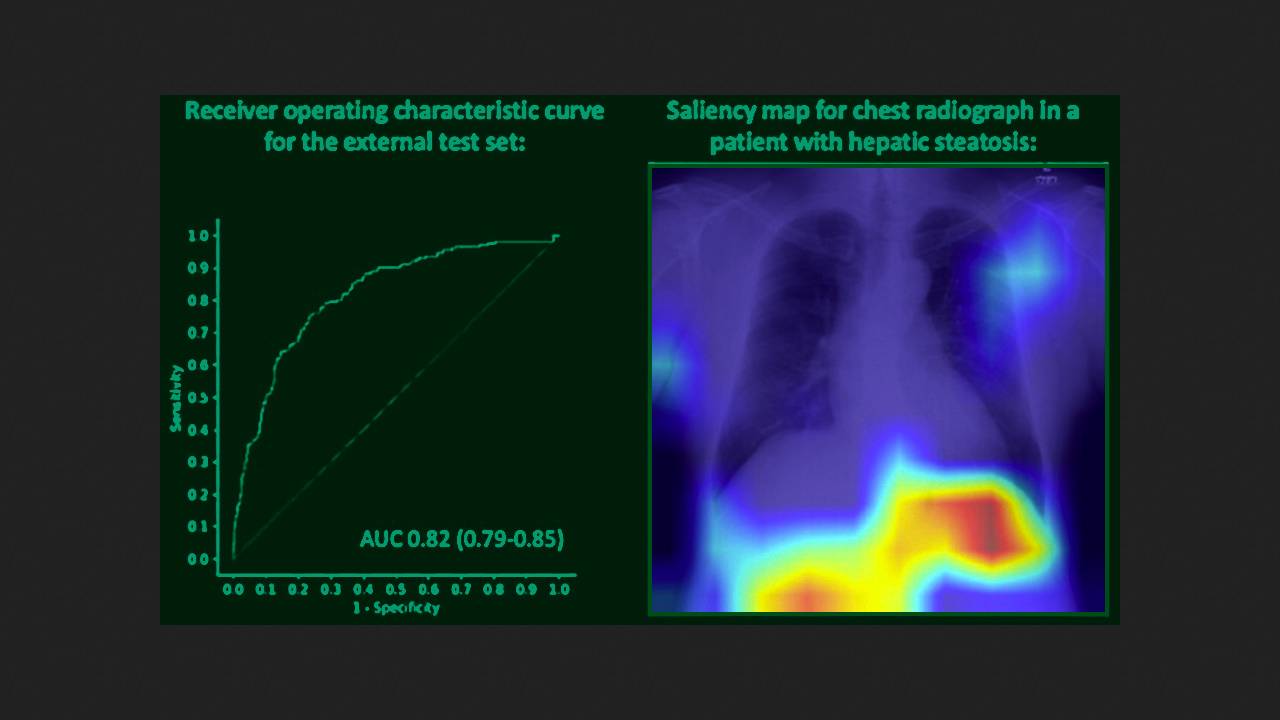
The dataset for internal testing included 529 chest radiographs from 363 patients (mean age 56 years; 344 men), and for external testing, 1,100 radiographs from 783 patients (mean age 58 years; 604 men). During internal testing, the area under the ROC curve was 0.83; accuracy was 77 percent; sensitivity was 68 percent; and specificity was 82 percent. For external testing, these figures were 0.82; 76, 76, and 76 percent, respectively. Model performance was rated as good.