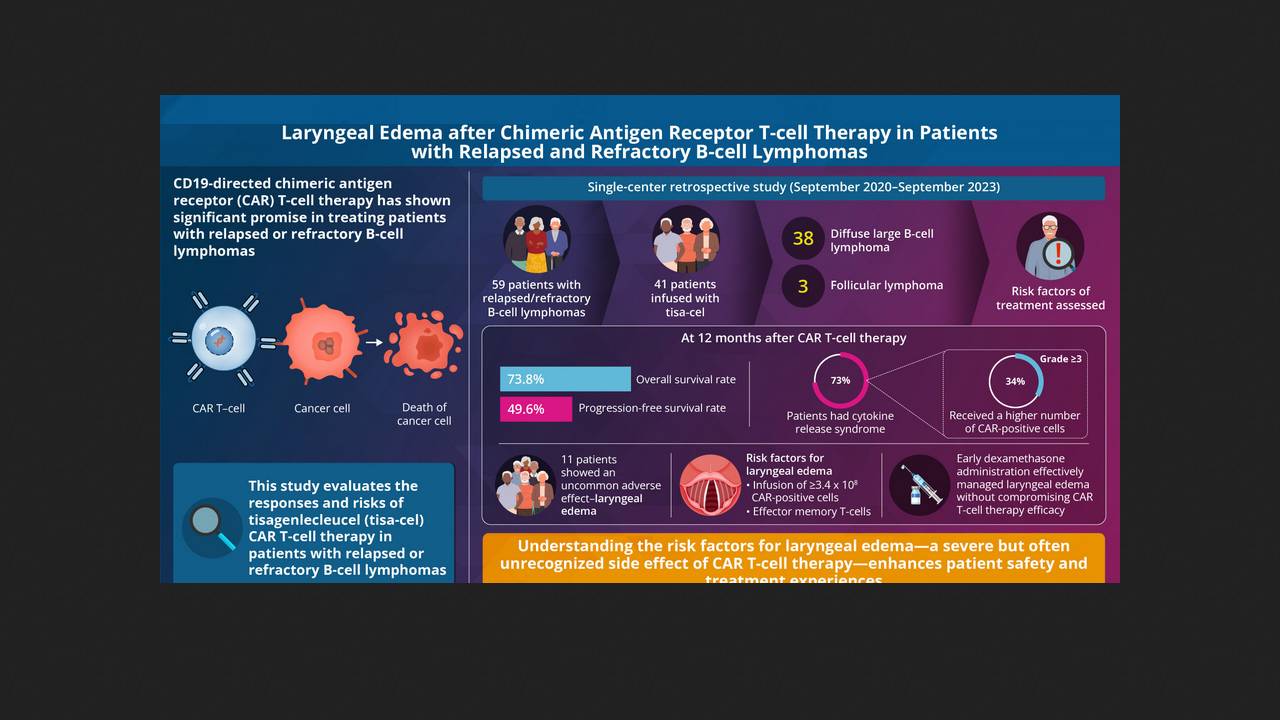
Erina Hosoya and colleagues at Juntendo University performed a retrospective analysis of data from 41 patients treated for B-cell lymphoma with the CAR-T cell drug tisagenlecleucel over three years. It revealed that 11 (27 percent) of the participants developed a serious side effect not recorded in previous studies. This was laryngeal edema, which can lead to airway compression and acute oxygen deprivation. It was independent of tumor location and was more common with infusions of more than 3.4 × 10 CAR-T cells. Timely dexamethasone therapy successfully managed this complication without affecting the efficacy of the therapy. The mechanisms underlying this complication remain unknown. The publication on this complication appeared in the journal Haematologica.
Among other side effects, the most common was the well-known cytokine release syndrome, which developed in 30 patients (73 percent), 14 of whom (34 percent) had a severe form. There were no treatment-related deaths. The overall survival rate was 73.8 percent, including 49.6 percent progression-free.